Key points from lecture
- Conformity
- Being watched subconsciously makes you act in a certain way
- Relies on surveillance , or at least that idea that you are always under surveillance
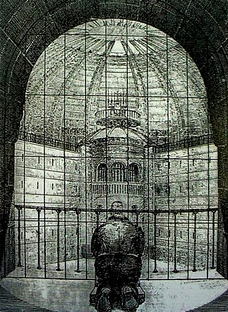
- Panopticon - Jeremy Bentham 1791 (political philosopher) Design - not particularly for prison
- Michel Foucault - Interested in the mechanism for discipline, Panopticon secluding people to be on their own, the way in which its a metaphor for the way society controls its citizens, an allergy of how we're controlled in our day to day lives. Panopticon symbolises our day to day lives. Figure for how we're controlled.
- Panopticon
- Isolation - Your own thoughts an lack of influence from anyone else, to one to relate to, can't plot, can't misbehave, gossip, stop working. IT begins the process of you internalising mentally of self discipline. The feeling of individualisation and isolation.
- Visibility - Unknown if someone's watching. Backlit. They are permanently lit, visible, puts them on display. The watcher visible.
- Behaviour and self control - Doesn't need anyone to exercise power over someone else, once internalised that your isolated, permanently visible, you conform to a set of idea that you think the person watching you wants to behave like. You start to control yourself.
- Surveillance
- Society - Shift from methods of physical control to much more subtle mental methods of control. Use of Asylum is where shift begins. Asylum - treats given as rewards, coersed subtly. First (ish) instance of modern disciplinary submerge. More effective to train people to behave than 'make' them.
- Physical control > Mental control (doesn't make it more humane) Old ways didn't correct the defects of people. Panopticon trains, and alters behaviour.
- Productive - e.g School - Panoptic system - makes children work harder, more focused. e.g Prison - Produces a form of behaviour in a person. E.g - Hospital - stop people spreading disease.
- Making people control themselves - Self regulation (as said by Foucault)
- Power - The power to control or exercise - Power is a relationship that we enter into willingly, Foucault thinks its a fiction that people have to use of someone else. Marxism and feminism - " theres a rule and class, in which the higher have power over the poor' ' Society is patriarchal, in which men have power over women' - Foucault - power only exists because a person lets themselves be exploited by such power. Panopticon - prisoners being exploited, people choosing to be controlled by tower, isolation etc to behave a certain way. Always a possibility of resistance (a lot of the time we don't see this opportunity and just conform).
- Panopticon makes your conform to the expected behaviour by the system, it disindivudualises the power relation - you never know the guard watching you, no personal relationship. Institutional gaze - e.g prison - act like the institution of law would want you to act like.
- For panopticism to work, there must always be a physical reminder. You can't be oblivious to it, otherwise it wouldn't work. E.g - Speed cameras - Visual reminder, may not even have a camera in. You become so trained you react to such visual reminders, and think nothing of it. Foucualts opinion - perfectly trained individual - 'Docile body'. Someone who won't resist and will conform. You don't question anything, you just act in a way.
- Method of control of supervised and supervisor.
Reading from Michel Foucault
Tasks: Analyse a piece within society which is panoptic (will be on blog)
Write about 300words - Choose some aspect of contemporary society which you think is panoptic / has a panoptic mechanism (e.g cctv) Polished piece of critical writing. Use technical terminology e.g docile body, self regulation. Weave five quotes from given text into the writing. Choose a fragment of a sentence to weave into my own writing. Don't skim read, read, read again, underline, use markers in margins etc. Highlight words I don't understand to look up later.
- CCTV (fake?) Fake security camera - LED light, to make it look like its working
- Speed cameras (is there even a camera in it)
- Suburban street - Houses facing onto road - can be seen by everyone, your garden can be seen my neighbours, feel the need to improve it. Feel its for their own pleasure - they're actually doing it as there aware someone is looking at it, to impress others.
- Open flan
- Teachers computer history is available.
Read and highlight given hand out - make notes 'Michel Foucault' - Panopticism
Makes notes on already highlighted areas
Bibliography to looks at - Michel Foucault - 'History of sexuality'
.....
TASK ONE
Response to task:
Subject matter: Modern technologies releasing your location
Quotations to use from 'Panoptism' handout by Michel Foucault
Plague; understood as a metaphor of social disorder; Foucault explains societies response to the threat of the plague as: 'a surveillance system of permanent registration: reports', a physical form of panopticism. Modern technologies, such as 'Google Maps' and Facebooks 'Places' app, allow us to invade others, to gain knowledge of their location, to subtly gain control unbeknown to the person, 'He is seen, but he does not see; he is the object'. As opposed to the panopticon, the 'inmate will constantly have before his eye the tall outline of the central tower', thus knowing they are possibly being watched upon, more so than those subject of such digital programs in the modern online age. We know such programs exist , but become, as Foucault describes as a 'Docile body', in conforming; allowing such information from being withheld; lacking to respond to such exploit of our privacy, becoming unresponsive, we fail to actually think about the affect such information could have in the hands of another, to ourselves.
Using the 'places' app; To give your 'Facebook friends' knowledge of your location, as a method of gaining feedback, to find and converse with others who find themselves within the same area. We fail to realise (Again relating to docility) the 'place' is released on the 'News feed' for all to see, it's become panoptic, 'Visibility is a trap'; the illusion to be open with your location, is some how protective, is a myth. It's a danger, once such information is realeased, you can't hide. In regard to 'Google maps', once an subject knows of your postcode, street, or city, it can be searched and looked upon. A panoptic view of someones house can be seen through a 'street view' option, it is a 'constant visability' to others. Such technologies are becoming panoptic and an intrusion to our privacy, yet, we don't react to it. For panopticism to work, there needs to be a physical reminder; the 'google maps' application works through word of mouth, through societys reliance on the internet. When visiting a new place, many of us immediately think to use the program, to then tell others the method in which we found the 'place', so there is a constant reminder of the ease of the programs use.